38-year-old male long-distance runner presents with chronic pain in both lower legs, worse on the right than the left.
bone scan with SPECT-CT of the lower limbs was performed.
Fig 1. Planar bone scan showing intense uptake in proximal right tibia and low grade uptake in medial left tibia.
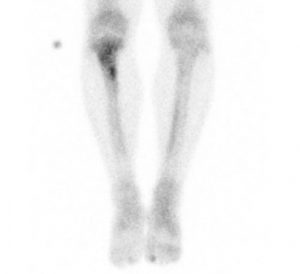
Fig 2a and 2b. Focal uptake in right proximal tibia with linear lucency on CT.
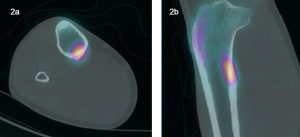
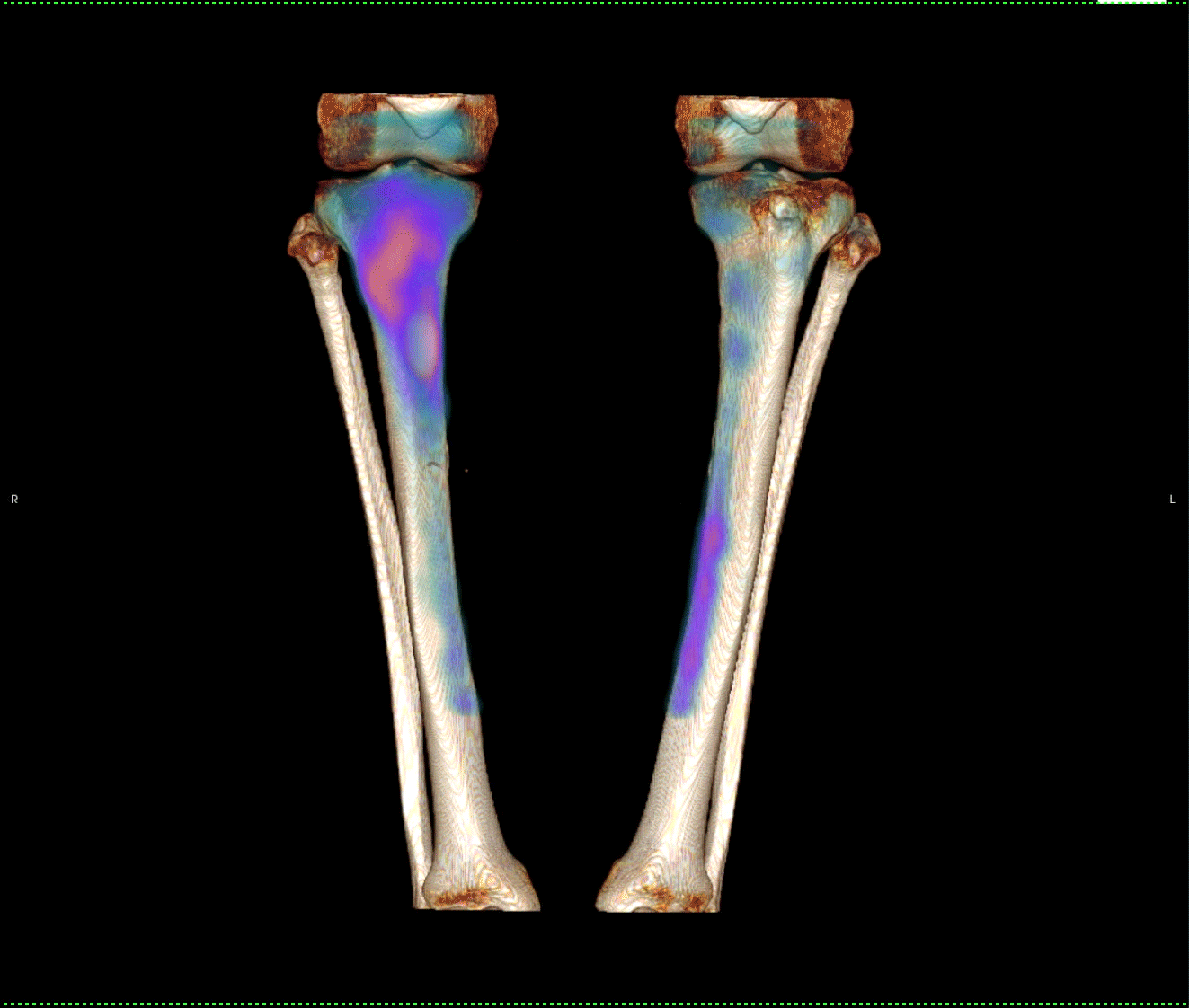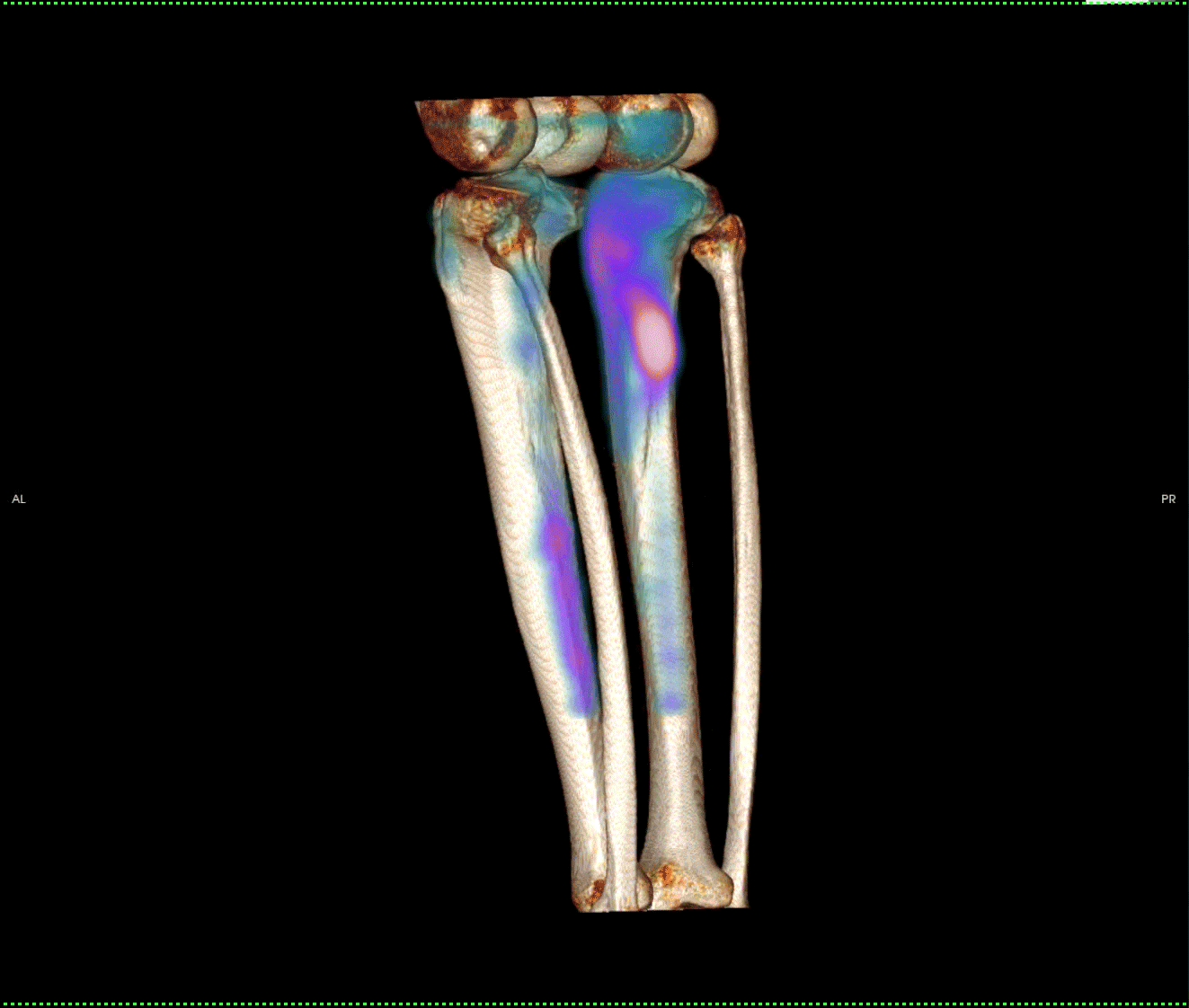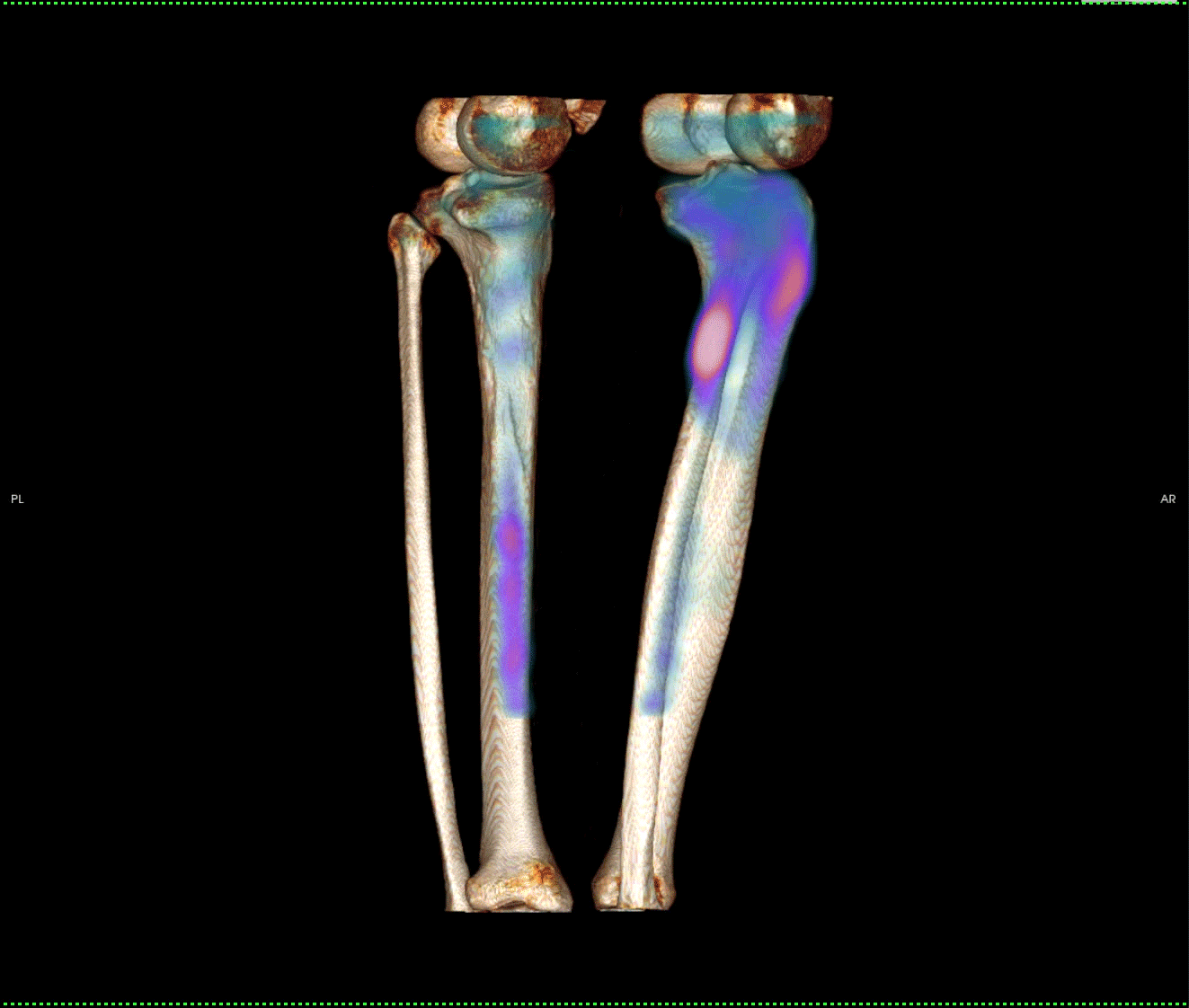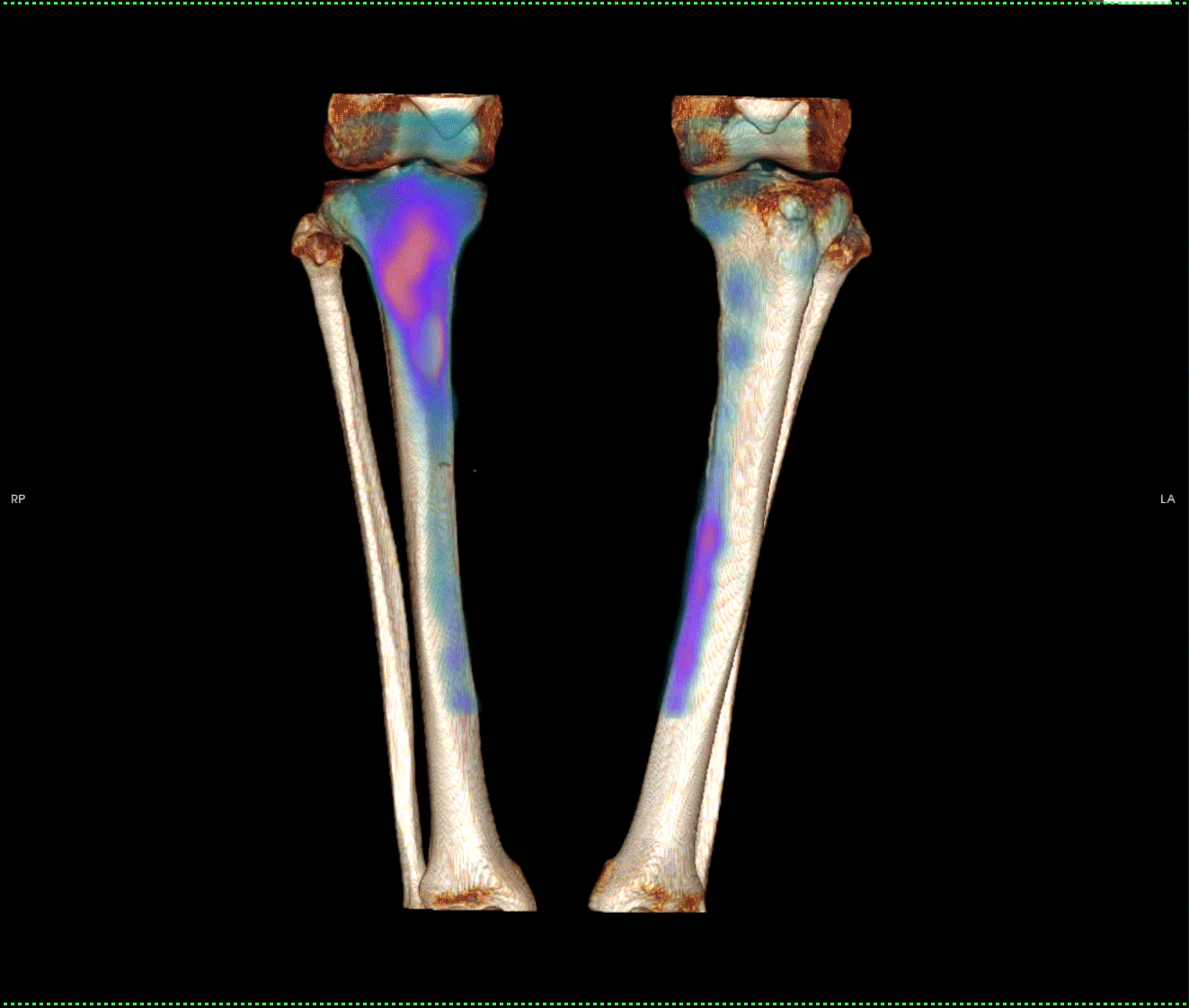
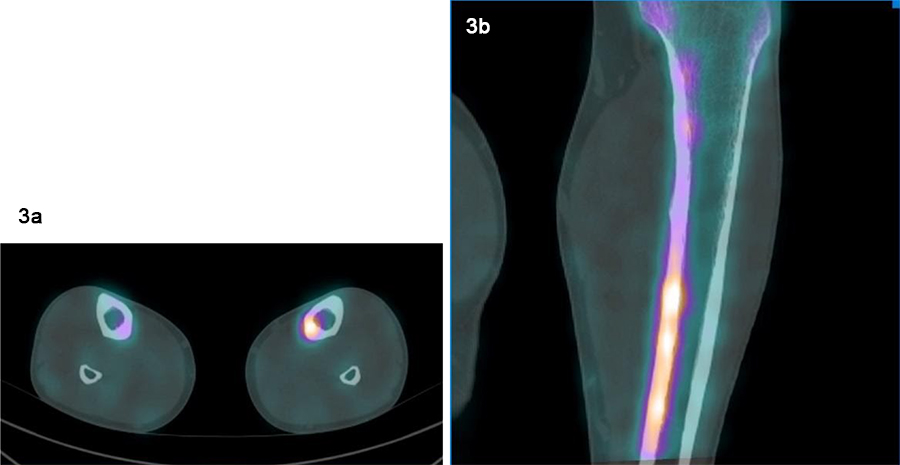
Fig 3a and 3b. Linear increased uptake in the posteromedial tibial shaft. Normal CT appearances.
Key findings
There is focal intense increase tracer uptake in the proximal right tibial cortex which corresponds to an oblique
linear lucency through the cortex.
In the left tibia there is linear low-grade tracer uptake longitudinally within the posteromedial tibial shaft. There is no focal abnormality on the CT component of the SPECT-CT in the left tibia.
Diagnosis
Right tibial stress fracture and left medial tibial stress syndrome.
Tibial Stress Fractures
Tibial stress fractures are small cracks in the cortex of the bone which are usually due to overuse and repetitive stress, such as due to long distance running. Tibial stress fractures can be differentiated from medial tibial stress syndrome on SPECT-CT by looking for the focal uptake that is typically transversely orientated to the tibial shaft. There will also be a corresponding fracture on CT and often a periosteal reaction.
Stress fractures are not treated surgically, but usually with rest and refraining from activity that causes pain.
Medial tibial stress syndrome
Medial tibial stress syndrome is also called “shin splints”. It usually presents with pain along the inner edge of the tibia, or shin bone. It is often associated with vigorous sporting activities such as running. Pain usually subsides after stopping activity. Treatment includes rest, but low-level activity can be maintained, as compared with stress fractures. Converting to lower impact types of activity can also be beneficial.
Bone scans have a high sensitivity for medial tibial stress syndrome, but SPECT-CT is useful to differentiate medial tibial stress syndrome from stress fractures. In medial tibial stress syndrome, there is linear uptake within the posteromedial tibial cortex that is longitudinally orientated to the tibial shaft. There will not be any abnormality seen on CT, which helps to distinguish it from a stress fracture.