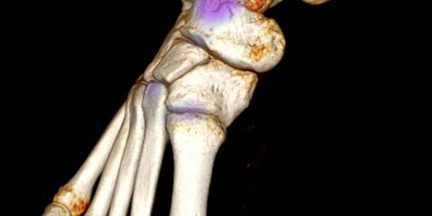
The ability to localise accurately sites of bone inflammation in the foot and ankle makes SPECT-CT an invaluable tool for many specialists in this area. Due to complex anatomy in the foot, it can sometimes be difficult to confidently diagnose the cause of pain, particularly in patients with previous trauma or chronic conditions such as diabetes. Traditional imaging modalities such as x-rays and MRI are often used in the initial work up of patients, but they have poor specificity and can often be abnormal even if the patient doesn’t have pain.
SPECT-CT relies on assessing bone turnover and therefore is much more specific in identifying the cause of patients’ pain.
SPECT-CT is often used in evaluating patients with degenerative disease of the joints in the ankle and foot. It can accurately localise the pain generator and allows surgeons to target the correct joint for steroid and local anaesthetic injection. It is often used in pre-operative planning to differentiate joints prior to surgical fusion. For instance, SPECT-CT is particularly useful in differentiating ankle joint from subtalar joint arthritis; something that can be challenging by clinical examination alone.
Our experience has shown that joint injections that are performed by targeting with SPECT-CT are more successful than injections performed without SPECT-CT guidance.
Parthipun A, Moser J, Mok W, Paramithas A, Hamilton P, Sott AH. 99mTc-HDP SPECT-CT Aids Localization of Joint Injections in Degenerative Joint Disease of the Foot and Ankle. Foot & Ankle International. 2015;36(8):928-935.
SPECT-CT is often used to assess the post-operative foot and ankle. It can correctly determine whether a treated fracture has healed or whether an attempted joint fusion has been successful. SPECT-CT does not suffer from the same metal artefact that plagues MRI scans, and therefore should be considered the gold standard investigation in the post-operative foot and ankle.

Finally, SPECT-CT can accurately diagnose impingement syndromes that can occur as a result of congenital or acquired deformities such as flat feet or accessory ossicles. The presence of abnormal tracer uptake can indicate that there is abnormal loading on the foot due to anatomical variation. This functional information cannot be determined by any another imaging modality.
Indications for SPECT-CT in the foot & ankle:
- Localising sites of symptomatic arthritis prior to intervention
- Assessing the post-surgical foot and ankle
- Evaluating union of fractures
- Identifying impingement syndromes
- Diagnosing symptomatic accessory ossicles